What Do You Need To Know About Checks And Balances?
Dec 04, 2024 By Kelly Walker
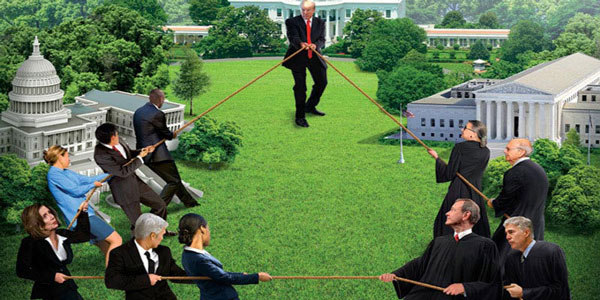
What Are Checks and Balances? Contemporary democracies rely heavily on a system of checks and balances. Referring to a form of government in which one branch or level of government can check and balance the authority of another. This system ensures that no one or group has complete control by preventing any one level of government from becoming too dominant. In this paper, I'll explain the concept of checks and balances, explain how they function, and discuss why they're crucial to working democracies today.
The Division Of Powers
One idea behind "checks and balances" is the separation of powers. This idea proposes that the government should be divided into separate bodies, all of which have their authority and responsibility. The executive, the legislature, and the judiciary are the three traditional arms of government in contemporary democracies.
Executive Branch
Law enforcement and implementation fall under the purview of the executive branch. The executive branch comprises the head of state, their cabinet, and other administrative agencies. The executive branch's authority is checked in several ways as part of a balanced system. Examples of these constraints are:
- The executive branch typically has veto authority over legislation passed by the legislature in modern democracies. The executive branch can use this authority to halt counterproductive or otherwise unsuitable legislation.
- Judicial Review: The judiciary, in many democracies, has the authority to examine executive branch activities to determine if they comply with the constitution or other legal principles.
Legislative Branch

It is the job of the legislature to create new statutes. Parliaments, congresses, and state and provincial legislatures are all included. As part of the system of checks and balances, the legislative branch's authority is limited in several ways. Some of these constraints include the following:
- The legislature can override a veto by the executive in most modern democracies. As a result of this authority, the legislature can enact laws against the opposition of the executive branch.
- In many democracies, the judicial branch can examine legislation to see if it complies with constitutional or other legal standards (a process known as judicial review).
- In several democracies, the executive branch appoints government positions and the judiciary, but the legislature must confirm those selections.
Judicial Branch
The judiciary is in charge of applying the law and settling disagreements. All judicial institutions are part of this sphere. Several Other Institutions and Mechanisms check the Judicial Branch's Power. Some of these constraints include the following:
- The judicial branch is supposed to display restraint and not meddle in the business of the other arms of government in several democracies.
- In many democracies, the judicial branch has the authority to examine the policies and procedures of the executive, legislative, and judicial departments to determine whether or not they adhere to the constitution and other legal principles.
- It is a fundamental principle of democracies that the judicial branch is free from political influence and can carry out its duties without interference.
Having Checks And Balances Is Essential

Those in charge do not act arbitrarily or unjustly toward citizens. In the United States, for instance, the right to free expression and due process of law are just two of the many individual liberties and safeguards enshrined in the Bill of Rights.
Thirdly, the system of checks and balances ensures that policy decisions are reached after careful consideration and compromise. A more collaborative and representative form of government is fostered through the design of "checks and balances," which necessitates the cooperation and mutual restraint of the several branches of government. If more people get their voices heard, it can lead to more informed decisions.
Conclusion
The system of checks and balances is a cornerstone of contemporary democracies. Referring to a form of government in which one branch or level of government can check and balance the authority of another. Essential to this structure is the separation of powers, which is why the administration, the legislature, and the judiciary each have their distinct roles. To ensure the long-term legitimacy and viability of democratic governance, and the protection of individual rights and freedoms, it is crucial to have a system of checks and balances in place.

At What Age Does Car Insurance Go Down? Types of Coverage

Understanding the Solutions Unbanked Population Worldwide

How to Get Your Overdraft Fees Refunded

A Detailed Overview of AARP

An Essential Guide to the Federal Sales Tax Deduction

How Much Money Can Day Traders Make?

How Much Time Is Required to Establish Good Credit From Beginning?

The Role of the US Dollar in Shaping Commodity Prices Across Markets

What Is a Solvency Capital Requirement (SCR)?

How to Get the Most of Your Social Security Benefits
What Do You Need To Know About Checks And Balances?
